Search
Content type: Examples
In July 2018, Robert Mueller, the special prosecutor appointed to look into Russian interference in the 2016 US presidential election, charged 12 Russian intelligence officers with hacking Hillary Clinton's campaign and the Democratic National Committee by spearphishing staffers. The charges include conspiracy to commit an offence against the US, aggravated identity theft, conspiracy to launder money, and conspiracy to access computers without authorisation. The hack led to the release of…
Content type: Examples
Facebook ads purchased in May 2016 by the Internet Research Agency, a notorious Russian troll farm, urged users to install the FaceMusic app. When installed, this Chrome extension gained wide access to the users' Facebook accounts and web browsing behaviour; in some cases it messaged all the user's Facebook Friends. The most successful of these ads specifically targeted American girls aged 14 to 17 and said the app would let them play their favourite music on Facebook for free and share it…
Content type: Examples
With only days to go before the 2018 US midterm elections, a federal judge ruled that the state of Georgia must change its "exact match" law that required voter registrations with even the tiniest variation from other official identifications to be flagged as potential non-citizens unless they could produce proof of identity. A group of civil rights groups sued Republican secretary of state Brian Kemp, in charge of the elections despite also running for governor, to change the procedure, which…
Content type: Examples
In August 2018, the US Democratic National Committee notified the FBI that the San Francisco-based security company Lookout and the cloud service provider DigitalOcean had detected an attempted hack targeted at the DNC voter database. The attack took the form of a fake DNC login page intended to trick people into disclosing their usernames and passwords thinking they were accessing the DNC's VoteBuilder platrform. Lookout believes it found the site within 30 minutes of its going up online, but…
Content type: Examples
Shortly before the 2018 US midterm elections, Georgia secretary of state and gubernatorial candidate Brian Kemp accused Georgia's Democratic Party of hacking into the state's voter registration database, though without providing any evidence to support the claim. The motives behind the claim were unclear, but a report published by WhoWhatWhy suggested that the claim may have referred to a cybersecurity investigation conducted by the Democrats that uncovered significant flaws in the state's…
Content type: Examples
In July 2018, Election Systems and Software (ES&S), long the top US manufacturer of voter machines, admitted in a letter to Senator Ron Wyden (D-OR) that it had installed pcAnywhere remote access software and modems on a number of the election management systems it had sold between 2000 and 2006. The admission was in direct contradiction to the company's response for a New York Times article earlier in the year on US voting machines' vulnerability to hacking. ES&S says it stopped…
Content type: Examples
In the run-up to the November 2018 US midterm elections, Vice tested Facebook's new system of mandatory "Paid for" disclosure intended to bring greater transparency to the sources of ads relating to "issues of national importance". Placing political ads requires a valid ID and proof of residence. Vice found that Facebook quickly approved ads the site attempted to place that named Islamic State, US vice president Mike Pence, and Democratic National Committee chair Tom Perez in the "Paid for"…
Content type: Examples
A combination of entrenched and litigious voting machine manufacturers with immense control over their proprietary software and a highly complex and fragmented voting infrastructure mean that even though concerns were raised as early as 2004 about the security of US voting machines, the 2018 midterm election saw little improvement. The machines in use in the more than 10,000 US election jurisdictions are all either optical-scan or direct-recording electronic (DRE). Optical-scan, which scans…
Content type: Examples
In September 2018, when Massachusetts state police tweeted a map of responses to fires and explosions during a gas emergency, they inadvertently revealed that they were closely monitoring several activist groups, including a Facebook group for Mass Action Against Police Brutality, the Coalition to Organize and Mobilize Boston Against Trump, Facebook 413, Facebook MA Activism, and Resistance Calendar. The image was taken down and cropped after half an hour, but it spurred journalists to ask…
Content type: Examples
In September 2018, Google warned a selection of US senators and their aides that their Gmail accounts were being targeted by foreign government hackers. Google has issued warnings of phishing attempts by state-sponsored actors since 2012, though getting a notice does not mean the account has been compromised.
https://www.cnet.com/news/google-warns-us-senators-of-foreign-hackers-targeting-their-gmail-accounts/
Writer: Richard Nieva
Publication: CNet
Content type: Examples
In the run-up to the 2018 US mid-term elections, researchers found that the dissemination of fake news on Facebook was increasingly a domestic American phenomenon rather than, as in the 2016 presidential election, an effort driven by state-backed Russian operatives. Removing such accounts (Twitter) and pages (Facebook) is tricky in the US, where the boundary between free speech and disinformation is particularly sensitive. In addition, domestic disinformation is harder to distinguish. One of…
Content type: Examples
In the months leading up to the US 2018 midterm elections, Republican officials in Georgia, Texas, and North Carolina made moves they described as ensuring voting integrity but which critics saw as blocking voter access. In Georgia, where Secretary of State Brian Kemp is charged with enforcing election law and was simultaneously running for governor, election officials blocked 53,000 applications to register, 70% of which are those of African-Americans, under a law requiring personal…
Content type: Examples
A few months before the US 2018 midterm elections, the Trump campaign team signed a contract with the newly-formed Virginia-based company Excelsior Strategies to exploit the first-party data the campaign had collected. The contract was set up by Trump's campaign manager, Brad Parscale, who built the list as the digital director of Trump's 2016 campaign and began renting it out soon after the November 2016 elections.
Subject to the Trump's campaign veto authority, Excelsior rents out this…
Content type: Examples
A little over a month before the US 2018 midterm elections, Twitter updated its rules to reduce manipulation of its platform. Among the changes, the company outlined the factors it would use to determine whether an account is fake and should be removed, provided an update on its automated detection and enforcement actions, and announced some changes to its user interface, which included reminding candidates to turn on two-factor authentication and encouraging US voters to register and vote.…
Content type: Advocacy
In September 2018, the National Executive sent the proposed Data Protection Bill to the National Congress. The proposed law was directed to the Senate and it will be considered by two commissions: the Commission of Constitutional Affairs (Comision de Asuntos Constitucionales) and the Commission of Rights and Guarantees (Comision de Derechos y Garantías).
Privacy International welcomes the continued efforts by Argentina to provide protections for the right to privacy, already enshrined in the…
Content type: News & Analysis
Taylor Swift may be tracking you, particularly if you were at her Rose Bowl show in May.
According to an article published by Vanity Fair, at Swift’s concert at the California stadium, fans were drawn to a kiosk where they could watch rehearsal clips. At the same time – and without their knowledge - facial-recognition cameras were scanning them, and the scans were then reportedly sent to a “command post” in Nashville, where they were compared to photos of people who are known…
Content type: News & Analysis
Creative Commons Photo Credit: Source
In September 2018, a month after Argentina lawmakers voted against the legalisation of abortion, we spoke to Eduardo Ferreyra from the Buenos Aires-based Asociacion por los Derechos Civiles about the role of privacy in the abortion debate. Also joining us in this second episode of the Gender and Privacy Series is Ambika Tandon from the Centre for Internet and Society in India to discuss the intersection between privacy and bodily autonomy.…
Content type: Examples
Days before the US November 2018 midterm elections, ProPublica discovered that an organisation called Energy4US spent $20,000 to run ads on Facebook pushing conservatives to support the Trump administration's reversal of fuel emission standards. On closer scrutiny, Energy4US appeared to be a front organisation for the trade association American Fuel and Petrochemical Manufacturers, which numbers the world's largest oil companies among its members. Although Facebook's announced requirement that…
Content type: Examples
In the run-up to the US 2018 mid-term elections, Facebook announced it would broaden the company's policies against voter suppression by banning misrepresentations about how to vote and whether a vote will be counted. The company also introduced a reporting option to allow users to report incorrect information and dedicated reporting channels for state election authorities. The company noted it was getting better at detecting and removing fake accounts and increasing transparency about…
Content type: Advocacy
Consumers benefit from the existence of competitive markets, in which they can freely choose among a wide range of products and services. Competition policy plays an important role in this regard by ensuring that competition is not disrupted in a way that can harm consumers directly (e.g. leading to price increases or less choice) or indirectly (e.g. weakening competition as a process by hampering the ability of firms to compete on the merits).
Content type: Examples
In May 2018, US Immigration and Customs Enforcement abandoned the development of machine learning software intended to mine Facebook, Twitter, and the open Internet to identify terrorists. The software, announced in the summer of 2017, had been a key element of president Donald Trump's "extreme vetting" programme and expected to flag at least 10,000 people a year for investigation. ICE decided instead to opt for a contractor who could provide training, management, and human personnel to do the…
Content type: News & Analysis
Our team wanted to see how data companies that are not used to being in the public spotlight would respond to people exercising their data rights. You have the right under the EU General Data Protection Regulation ("GDPR") to demand that companies operating in the European Union (either because they are based here or target their products or services to individuals in the EU) delete your data within one month. We wrote to seven companies and requested that they delete our data, and we've made…
Content type: Advocacy
Today, Privacy International has filed complaints against seven data brokers (Acxiom, Oracle), ad-tech companies (Criteo, Quantcast, Tapad), and credit referencing agencies (Equifax, Experian) with data protection authorities in France, Ireland, and the UK.
It’s been more than five months since the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) came into effect. Fundamentally, the GDPR strengthens rights of individuals with regard to the protection of their data, imposes more…
Content type: News & Analysis
Image Source
On 10 October 2018, the US Senate Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation, will convene a hearing titled “Consumer Data Privacy: Examining Lessons From the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation and the California Consumer Privacy Act".
The Senate will hear from:
Dr. Andrea Jelinek, Chair, European Data Protection Board
Mr. Alastair Mactaggart, Board Chair, Californians for Consumer Privacy
Ms. Laura Moy, Executive Director and Adjunct…
Content type: News & Analysis
Image attribution: By Blue Diamond Gallery CC BY-SA 3.0.
In March 2017, when the UN Human Rights Council requested the High Commissioner for Human Rights to prepare a report on the right to privacy in the digital age, including the responsibility of business enterprises, Cambridge Analytica was an obscure company among others. A year later the data exploitation scandal erupted, leading to plenty of soul searching by politicians in US, UK, Europe and elsewhere, pledges of…
Content type: News & Analysis
This piece was originally published on Just Security.
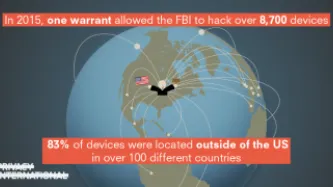
Ten years ago, an FBI official impersonated an Associated Press reporter to lure and track a teenager suspected of sending in prank bomb threats to his school. To find him, the FBI agent, posing as a reporter, sent the teenager links to a supposed story he was working on, but the links were infested with malware that once clicked on quickly exposed the teen’s location. More recently, the FBI has seized and modified websites so…
Content type: News & Analysis
Creative Commons Photo Credit: Source
Just about everyone in Washington has found something to dislike about the tech industry: Democrats especially, are worried about foreign interference in the 2016 election — meanwhile some Republicans are more concerned about bias against conservatives of platforms and on top of it all President Trump has been tweeting about antitrust and competition.
Privacy International is a vocal critic of data exploitation more generally, and the systemic…
Content type: News & Analysis
Around the world, from North America to Europe and Asia, governments are starting to roll out smart meters. While the technology promises increased energy efficiency through greater consumer control over energy consumption, smart meters also raise serious privacy concerns. Smart meters collect energy usage data at high frequencies - typically every five, fifteen or 30 minutes. That level of granularity reveals how much electricity is being used in a home and when, which in turn can paint an…
Content type: News & Analysis
This piece originally appeared here.
Creative Commons Photo Credit: Source
Tech competition is being used to push a dangerous corporate agenda.
High-tech industries have become the new battlefield as the United States and China clash over tariffs and trade deficits. It’s a new truism that the two countries are locked in a race for dominance in artificial intelligence and that data could drive the outcome.
In this purported race for technological high ground, the argument often goes, China…
Content type: Long Read
Creative Commons Photo Credit: Source
In the midst of continued widespread public outrage at the US government’s brutal ‘zero-tolerance’ policy around immigration – multiple data and analytics companies have quietly avoided answering questions about their role in feeding the US Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) agency’s data backbone. These companies are bidding to work with an agency that has time and time again shown itself to be a brutal and problematic.
Privacy International…