Search
Content type: Advocacy
As we come to the end of 2019, major weaknesses remain with the transparency that all major platforms have so far provided to users. This piece will overview these weaknesses and suggest steps to move forward in 2020.
Tying heightened transparency to "political" ads introduces a variety of problems. For a start, each platform has defined "political" differently, with some having wider definitions and some, incredibly narrow. When an ad is not designated as political, oftentimes it is provided…
Content type: Long Read
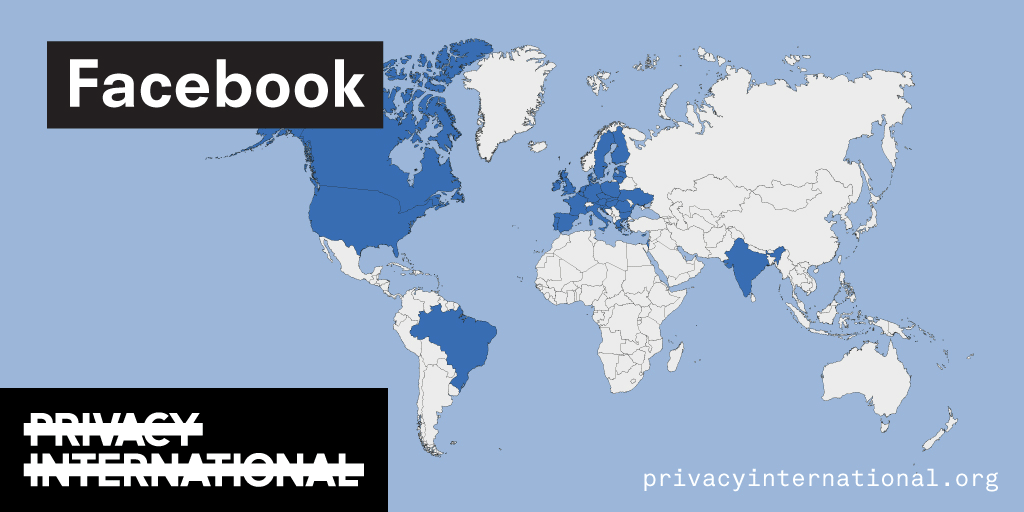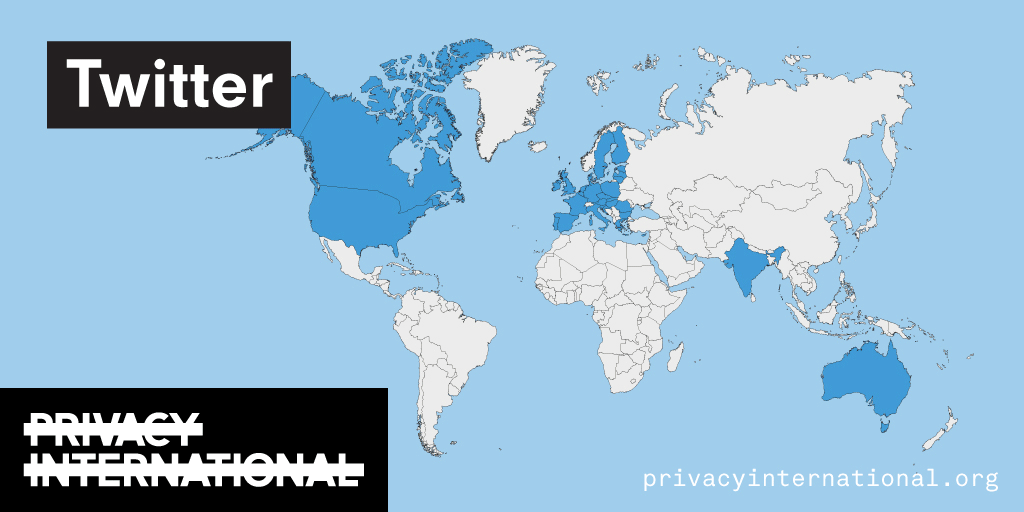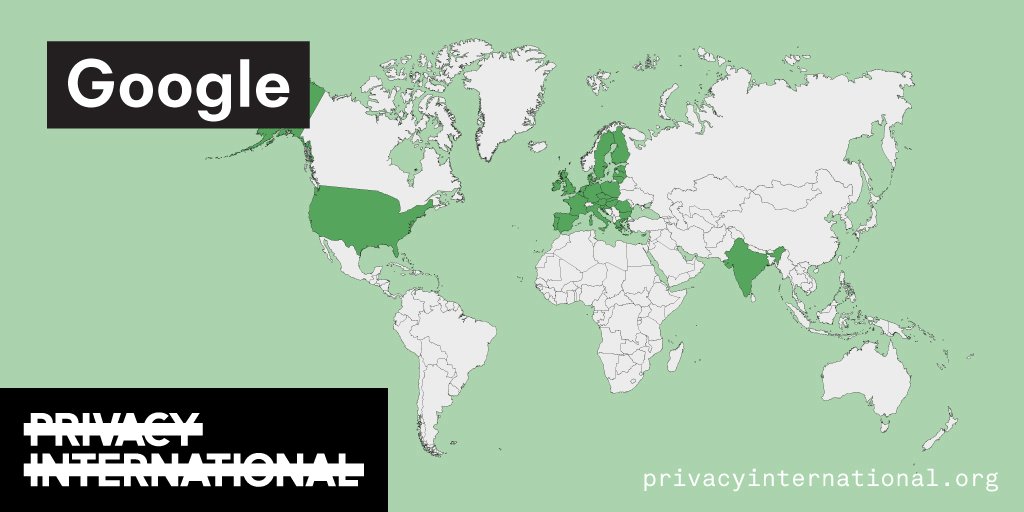
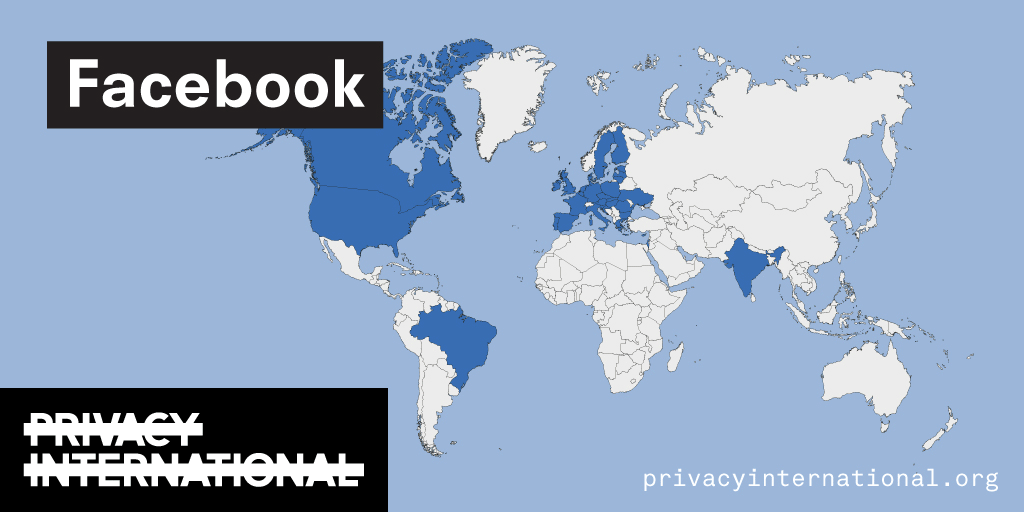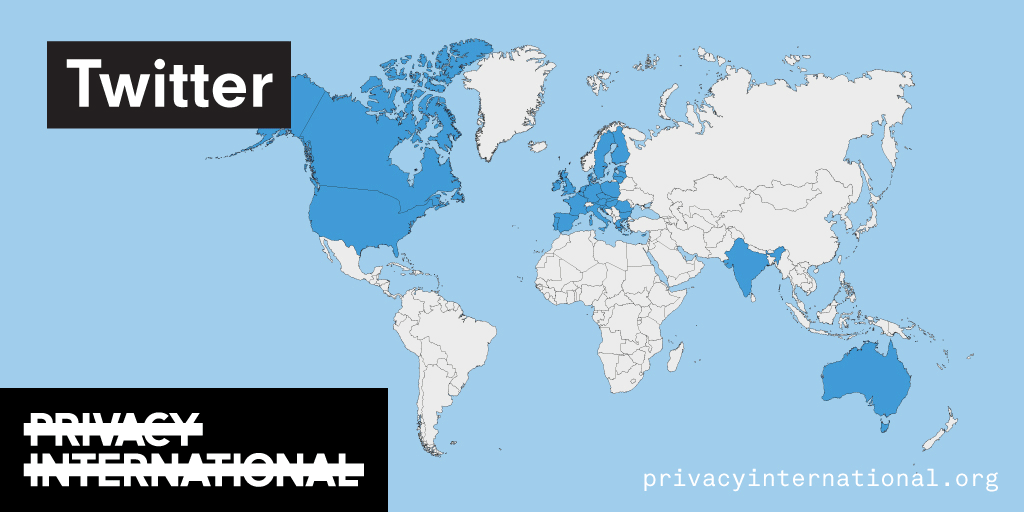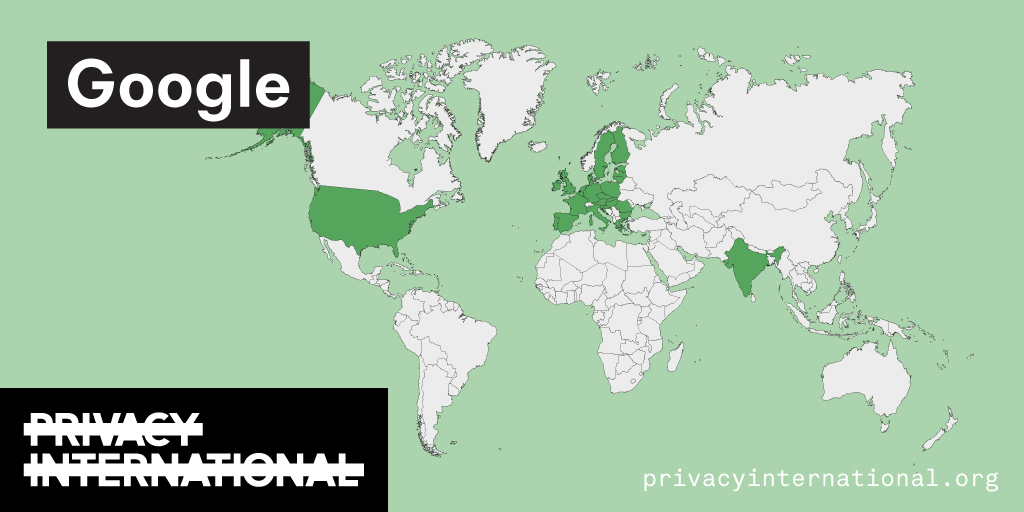
An analysis of what Facebook, Google, and Twitter have done to provide users with political ad transparency as of September 2019. Our full analysis is linked below.
Recently the role of social media and search platforms in political campaigning and elections has come under scrutiny. Concerns range from the spread of disinformation, to profiling of users without their knowledge, to micro-targeting of users with tailored messages, to interference by foreign entities, and more. Significant…
Content type: Long Read
We found this image here.
Using Facebook, Google, and Twitter’s ad libraries, PI has tried to understand how political ads are targeted in the UK. This information – which should be very clear on political ads – is instead being squirreled away under multiple clicks and confusing headings.
Importantly, in most countries around the world, users cannot understand why they’re being targeted with political ads on these platforms at all. This is because Facebook, Google, and Twitter have taken…
Content type: Advocacy
On 28 August 2019 PI joined International Privacy Network partner Asociación por los Derechos Civiles and others in writing to the Directors of Public Policy for Latin America at Facebook, Google, and Twitter. The letters outline what steps are needed to make the social media giants' ad archives effective. Earlier this year organisations across Europe, led by the Mozilla, wrote to the companies with similar guidelines - the letters sent today say that equivalent steps should be taken for ad…
Content type: Explainer
Recently the role of social media and search platforms in political campaigning and elections has come under scrutiny. Concerns range from the spread of disinformation, to profiling of users without their knowledge, to micro-targeting of users with tailored messages, to interference by foreign entities, and more. Significant attention has been paid to the transparency of political ads - what are companies doing to provide their users globally with meaningful transparency into how they…
Content type: Examples
In an effort to improve political advertising transparency, Canada drafted a Bill that requires companies to develop ad libraries, to which ads are added immediately in order for researchers, journalists, and other people to be able to search and understand how political actors are targeting ads. In response, Google announced that it would blanket-ban all political ads in Canada, saying the company was unable to comply with the new law. Google’s decision shows both that the current state of…
Content type: Examples
The two leading Presidential candidates in Ukraine's 2019 elections have expressed frustration at major social media platform's seemingly lack of assistance combatting disinformation and bots. Bots flood social media networks and can promote content or flood platforms with pull requests to have a piece of content taken down. Campaigns are unable to directly contact Google, YouTube, and Facebook for assistance directly and waste resources constantly fighting against bot armies.
https://www.…
Content type: Long Read
Image Source: "Voting Key" by CreditDebitPro is licensed under CC BY 2.0
Democratic society is under threat from a range of players exploiting our data in ways which are often hidden and unaccountable. These actors are manifold: traditional political parties (from the whole political spectrum), organisations or individuals pushing particular political agendas, foreign actors aiming at interfering with national democratic processes, and the industries that provide products that …
Content type: News & Analysis
The first half of 2018 saw two major privacy moments: in March, the Facebook/ Cambridge Analytica scandal broke, followed in May by the EU General Data Protection Regulation ("GDPR") taking effect. The Cambridge Analytica scandal, as it has become known, grabbed the attention and outrage of the media, the public, parliamentarians and regulators around the world - demonstrating that yes, people do care about violations of their privacy and abuse of power. This scandal has been one of…
Content type: Examples
According to research conducted by Ronan Chardonneau, a French associate professor of digital marketing at Angers University, none of the websites of the eleven candidates' in the 2017 French presidential elections, that he looked into respected CNIL's directives regarding information that should be available on the website and consent requirements for data collection. According to this research, nine of the candidates used Google Analytics, without activating the option to anonymize data…
Content type: News & Analysis
Photo by DAVID ILIFF. License: CC-BY-SA 3.0
Between 23 and 26 May 2019 Europeans will be voting to elect members of the European Parliament.
Since the last elections in 2014, much has changed within and without the European Union: the rise of nationalism and Euroscepticism, the protracted armed conflict in Ukraine and the occupation of Crimea by Russia, the new political orientation of the United States, just to name a few.
Among the new challenges facing these elections is…
Content type: Long Read
“Truth exists, but you have to find it”, Oleksandra Matviychuk of Ukraine’s Center for Civil Liberties told me as I interviewed her in central Kyiv one week before the 2019 Ukrainian run-off election, “and in order to do so you have to make some effort”. We’re talking about her experience working on the ground in Ukraine, a country with a long history of battling against disinformation.
Activists in Ukraine have long experience navigating the noisy and chaotic environment that disinformation…
Content type: Long Read
This image was found here.
Spain is holding a national general election on April 28 (its third in four years). Four weeks later Spaniards will again go to the polls to vote in the European Parliament elections. At Privacy International we are working to investigate and challenge the exploitation of people’s data in the electoral cycle including in political campaigns. This includes looking at the legal frameworks governing the use of data by political parties and their…
Content type: Examples
A December 2018 report prepared by the Oxford Internet Institute's Computational propaganda Research Project and the network analysis firm Graphika for the US Senate Intelligence Committee found that the campaign conducted by Russia's Internet Research Agency during the 2016 US presidential election used every major social media platform to deliver messages in words, images, and videos to help elect Donald Trump - and stepped up efforts to support him once he assumed office. The report relied…
Content type: Examples
In the run-up to the May 2019 European Parliament elections, Google announced it would launch a new set of transparency tools to combat voter manipulation. Before being allowed to buy advertising on Google platforms, campaigns will be required to verify their identity, and approved ads will be required to display the identity of their purchaser. Google will build a real-time searchable database of all political ads and show their purchasers, costs, and demographics. Facebook announced similar…
Content type: News & Analysis
PI has today written to Google, Instagram, Snapchat, TicTok, Twitter, YouTube, and WhatsApp to ask for more information about their steps to tell people why they are seeing ads. Facebook recently announced expanding the company's ad transparency measures to include more information about why an ad or content appears in a user's newsfeed. While Facebook has a lot more to do, it is important that all technology companies provide advertising transparency.
Recently, we have seen how platforms…
Content type: News & Analysis
Privacy International welcomes the focus on data and privacy contained in the final report by the UK House of Commons Digital, Culture, Media and Sport Committee (DCMS) on Disinformation and ‘fake news’. Beyond our control, companies and political parties have banded together to exploit our data. This report establishes essential steps to remedying this downward spiral. An important part of the democratic process is freedom of expression and right to political participation, including the right…